Actinometry#
Load Experimental Actinometry Data#
We begin by importing the required library and loading the actinometry measurement data from a CSV file. The dataset is stored in exp_data for further analysis
import pandas as pd # Import the pandas library for data handling
# Load the actinometry experiment data from the specified CSV file
exp_data = pd.read_csv("DATA/DAE.csv")
exp_data # Display the loaded dataset
| timestamp | cycle | type | 186.85486 | 187.31995223015844 | 187.78500323297956 | 188.250012996982 | 188.71498151068454 | 189.17990876260572 | 189.64479474126426 | ... | 1032.9632529736894 | 1033.3204920667242 | 1033.6776665334785 | 1034.034776362471 | 1034.3918215422202 | 1034.7488020612445 | 1035.1057179080635 | 1035.4625690711953 | 1035.8193555391586 | 1036.176077300472 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 2025-04-04 11:29:32.797890 | 1 | zero | 16.990556 | 24978.543889 | 249.154361 | 241.872694 | 253.523361 | 243.935833 | 258.499167 | ... | 652.315972 | 654.500472 | 655.471361 | 647.218806 | 664.694806 | 659.354917 | 666.151139 | 657.049056 | 657.049056 | 657.049056 |
| 1 | 2025-04-04 11:31:06.034842 | 1 | on | 16.990556 | 24978.543889 | 254.858333 | 231.395185 | 276.163951 | 261.600617 | 252.431111 | ... | 639.168519 | 672.070864 | 642.944198 | 664.789198 | 651.034938 | 650.495556 | 633.235309 | 639.707901 | 639.707901 | 639.707901 |
| 2 | 2025-04-04 11:31:07.075687 | 1 | on | 16.990556 | 24978.543889 | 240.025309 | 238.676852 | 256.206790 | 239.755617 | 265.106605 | ... | 653.192469 | 652.922778 | 643.483580 | 663.710432 | 668.834568 | 634.853457 | 628.111173 | 670.452716 | 670.452716 | 670.452716 |
| 3 | 2025-04-04 11:31:08.109308 | 1 | on | 16.990556 | 24978.543889 | 242.991914 | 246.767593 | 242.182840 | 280.479012 | 280.748704 | ... | 637.820062 | 659.665062 | 663.440741 | 645.641111 | 635.662531 | 629.189938 | 638.359444 | 631.347469 | 631.347469 | 631.347469 |
| 4 | 2025-04-04 11:31:09.153691 | 1 | on | 16.990556 | 24978.543889 | 241.643457 | 222.765062 | 271.039815 | 262.140000 | 255.667407 | ... | 652.113704 | 651.844012 | 651.574321 | 651.034938 | 648.877407 | 647.528951 | 638.629136 | 645.101728 | 645.101728 | 645.101728 |
| ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... |
| 614 | 2025-04-04 11:41:43.804611 | 1 | on | 16.990556 | 24978.543889 | 241.913148 | 236.789012 | 220.337840 | 231.934568 | 246.767593 | ... | 649.686481 | 641.326049 | 641.865432 | 641.865432 | 641.056358 | 645.371420 | 639.438210 | 631.347469 | 631.347469 | 631.347469 |
| 615 | 2025-04-04 11:41:44.858569 | 1 | on | 16.990556 | 24978.543889 | 212.786481 | 231.125494 | 234.361790 | 239.755617 | 265.106605 | ... | 638.089753 | 626.762716 | 630.268704 | 636.201914 | 634.853457 | 648.068333 | 654.001543 | 662.361975 | 662.361975 | 662.361975 |
| 616 | 2025-04-04 11:41:45.888795 | 1 | on | 16.990556 | 24978.543889 | 223.304444 | 240.564691 | 237.058704 | 251.622037 | 240.295000 | ... | 659.125679 | 635.392840 | 641.056358 | 646.719877 | 642.135123 | 654.540926 | 630.268704 | 648.338025 | 648.338025 | 648.338025 |
| 617 | 2025-04-04 11:41:46.925455 | 1 | on | 16.990556 | 24978.543889 | 232.204259 | 234.631481 | 235.170864 | 257.824938 | 243.800988 | ... | 621.368889 | 644.292654 | 632.156543 | 629.459630 | 631.617160 | 652.653086 | 630.808086 | 632.426235 | 632.426235 | 632.426235 |
| 618 | 2025-04-04 11:41:59.961864 | 1 | static | 16.990556 | 24978.543889 | 225.488944 | 217.964556 | 231.557000 | 247.455306 | 278.281028 | ... | 634.475889 | 630.228250 | 649.888750 | 648.675139 | 633.990444 | 646.247917 | 634.111806 | 643.213889 | 643.213889 | 643.213889 |
619 rows × 2051 columns
Preprocess Spectral Data and Compute Absorbance#
We now prepare the spectral intensity data for analysis. The dataset contains different types of measurements:
“zero”: baseline measurements,
“static”: background noise or dark reference,
Other types: actual actinometry measurements over time.
We extract these components, convert timestamps, and compute the absorbance spectrum using the formula:
$$A(\lambda) = -\log_{10} \left( \frac{I(\lambda) - I_{\text{static}}(\lambda)}{I_{\text{zero}}(\lambda) - I_{\text{static}}(\lambda)} \right)$$
This normalization corrects for both dark current and reference intensity variations.
import numpy as np # NumPy for numerical operations
# Extract intensity data excluding 'zero' and 'static' types
intensities = np.array(
exp_data[(exp_data["type"] != "zero") & (exp_data["type"] != "static")].iloc[:, 3:],
dtype=np.float64
)
# Extract static (dark) reference spectrum
static = np.array(
exp_data[exp_data["type"] == "static"].iloc[:, 3:],
dtype=np.float64
)[0]
# Extract zero (reference light) spectrum
zero = np.array(
exp_data[exp_data["type"] == "zero"].iloc[:, 3:],
dtype=np.float64
)[0]
# Extract wavelengths from column names (assuming columns 3+ are spectral data)
wavelengths = np.array(exp_data.columns[3:], dtype=np.float64)
# Convert timestamp strings to seconds since the first measurement
timestamps = pd.to_datetime(
exp_data["timestamp"][(exp_data["type"] != "zero") & (exp_data["type"] != "static")]
)
timestamps = np.array((timestamps - timestamps.iloc[0]).dt.total_seconds())
# Function to compute absorbance spectrum
def compute_absorbance(intensities: np.ndarray, static: np.ndarray, zero: np.ndarray) -> np.ndarray:
EPS = 1e-12 # Small epsilon to avoid division by zero or log of zero
num = intensities - static
den = np.maximum(zero - static, EPS) # Ensure denominator is not zero
absorbance = -np.log10(np.maximum(num / den, EPS)) # Log transform with safety check
return absorbance
# Calculate absorbance for each measurement
absorbance = compute_absorbance(intensities, static, zero)
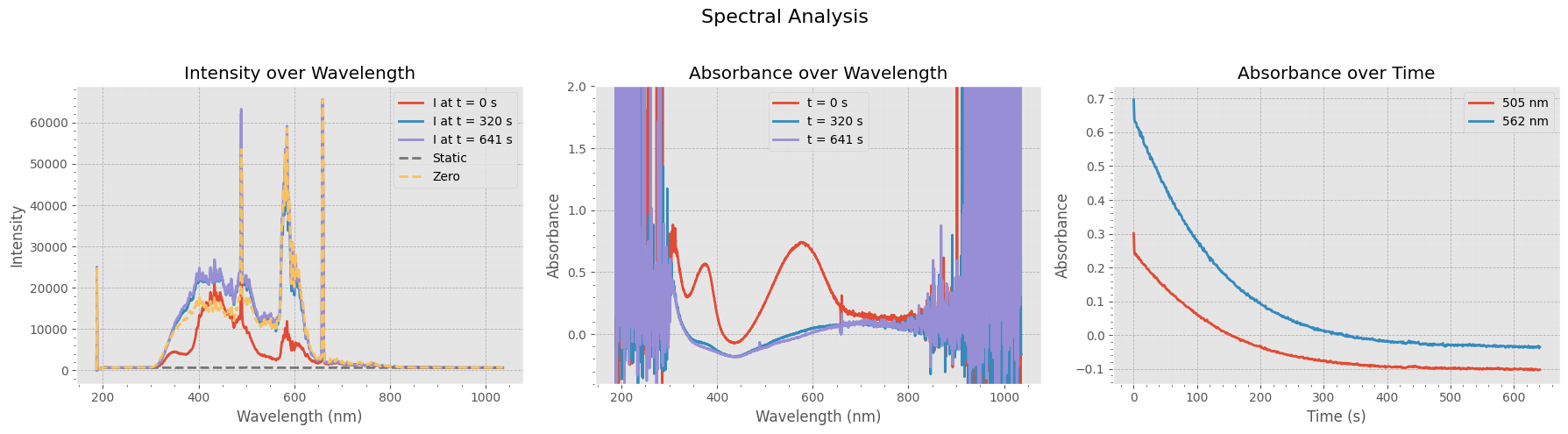
Visualizing Spectral Intensity and Absorbance#
This figure provides a comprehensive view of the actinometry data:
Left Panel: Raw intensity spectra at three time points, along with the static and zero references.
Middle Panel: Corresponding absorbance spectra at the same time points, showing how absorption evolves over time.
Right Panel: Absorbance at two key wavelengths (505 nm and 562 nm) plotted as a function of time, highlighting dynamic changes in the sample.
These plots help assess the stability and dynamics of the measured signals and the quality of the zero/static references.
Show code cell source
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.cm as cm
# Use a clean, readable plotting style
plt.style.use("ggplot")
# Set up a figure with 3 subplots side by side
fig, axs = plt.subplots(1, 3, figsize=(18, 5))
fig.suptitle("Spectral Analysis", fontsize=16)
# === Plot 1: Raw Intensities ===
# Show intensity at beginning, middle, and end of acquisition
axs[0].plot(wavelengths, intensities[0, :], label=f"I at t = {timestamps[0]:.0f} s", linewidth=2)
axs[0].plot(wavelengths, intensities[len(intensities)//2, :], label=f"I at t = {timestamps[len(intensities)//2]:.0f} s", linewidth=2)
axs[0].plot(wavelengths, intensities[-1, :], label=f"I at t = {timestamps[-1]:.0f} s", linewidth=2)
# Add static and zero reference spectra for comparison
axs[0].plot(wavelengths, static, '--', label="Static", linewidth=2)
axs[0].plot(wavelengths, zero, '--', label="Zero", linewidth=2)
axs[0].set_title("Intensity over Wavelength")
axs[0].set_xlabel("Wavelength (nm)")
axs[0].set_ylabel("Intensity")
axs[0].legend()
# Add major and minor grid for clarity
axs[0].grid(True, which='major', linestyle='--', linewidth=0.6, color='gray', alpha=0.5, zorder=0)
axs[0].minorticks_on()
axs[0].grid(True, which='minor', linestyle=':', linewidth=0.3, color='lightgray', alpha=0.4, zorder=0)
# === Plot 2: Absorbance Spectra ===
# Show absorbance at beginning, middle, and end of acquisition
axs[1].plot(wavelengths, absorbance[0, :], label=f"t = {timestamps[0]:.0f} s", linewidth=2)
axs[1].plot(wavelengths, absorbance[len(absorbance)//2, :], label=f"t = {timestamps[len(absorbance)//2]:.0f} s", linewidth=2)
axs[1].plot(wavelengths, absorbance[-1, :], label=f"t = {timestamps[-1]:.0f} s", linewidth=2)
axs[1].set_title("Absorbance over Wavelength")
axs[1].set_xlabel("Wavelength (nm)")
axs[1].set_ylabel("Absorbance")
axs[1].set_ylim(-0.4, 2)
axs[1].legend()
# Grid setup
axs[1].grid(True, which='major', linestyle='--', linewidth=0.6, color='gray', alpha=0.5, zorder=0)
axs[1].minorticks_on()
axs[1].grid(True, which='minor', linestyle=':', linewidth=0.3, color='lightgray', alpha=0.4, zorder=0)
# === Plot 3: Absorbance vs Time at Key Wavelengths ===
# Choose wavelengths of interest (e.g. peaks)
WL = [505, 562]
idxs = [np.argmin(np.abs(wavelengths - wl)) for wl in WL] # Find closest actual wavelength index
# Plot absorbance vs time for selected wavelengths
for i, idx in enumerate(idxs):
axs[2].plot(timestamps, absorbance[:, idx], label=f"{wavelengths[idx]:.0f} nm", linewidth=2)
axs[2].set_title("Absorbance over Time")
axs[2].set_xlabel("Time (s)")
axs[2].set_ylabel("Absorbance")
axs[2].legend()
# Grid setup
axs[2].grid(True, which='major', linestyle='--', linewidth=0.6, color='gray', alpha=0.5, zorder=0)
axs[2].minorticks_on()
axs[2].grid(True, which='minor', linestyle=':', linewidth=0.3, color='lightgray', alpha=0.4, zorder=0)
# Adjust layout to prevent overlap
plt.tight_layout(rect=[0, 0, 1, 0.95])
plt.show()
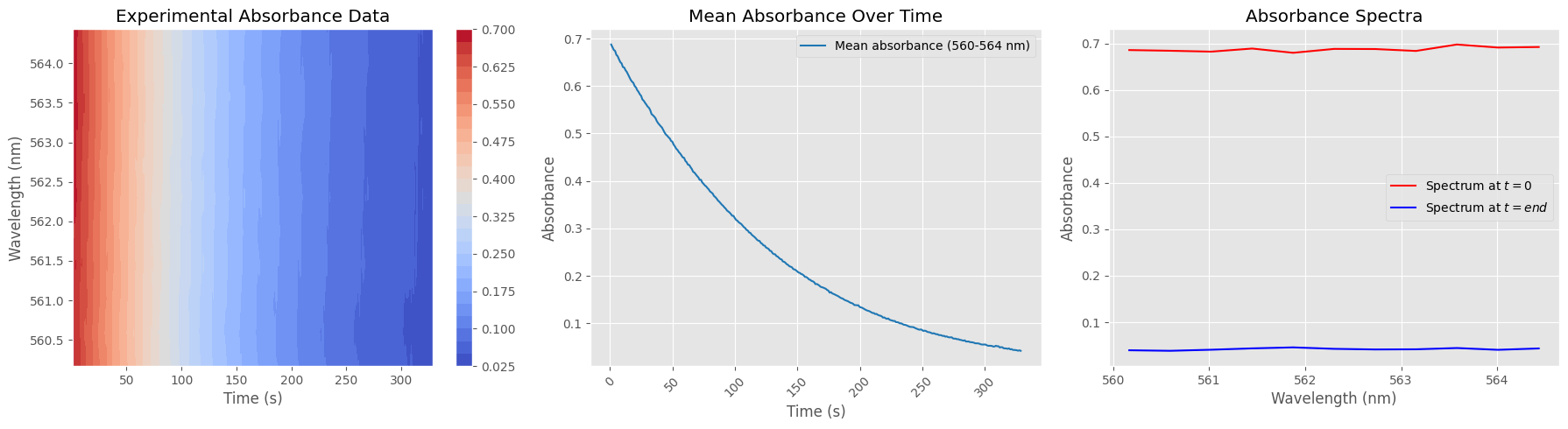
Data Cleaning and Absorbance Subset Preparation#
This cell prepares the dataset for focused analysis by:
Selecting a narrow wavelength range (e.g. 560–565 nm)
Normalizing absorbance values
Removing unwanted time points (first spectrum and last 300)
The resulting cleaned subset is suitable for targeted visualization or kinetic analysis.
# === USER PARAMETERS ===
wavelength_range = [560, 565] # Wavelength range of interest (nm)
remove_first = True # Whether to remove the first time point
remove_last_n = 300 # Number of last time points to remove
time_filter_indices = [0] + list(range(-300, 0))
# === Select wavelength index range ===
idx_range = np.argmin(np.abs(wavelengths[:, None] - wavelength_range), axis=0)
# Extract absorbance data in selected range
absorbance_subset = absorbance[:, idx_range[0]:idx_range[1]]
absorbance_subset -= np.min(absorbance_subset) # Normalize (set min to 0)
# Corresponding wavelengths
wavelengths_subset = wavelengths[idx_range[0]:idx_range[1]]
# === Filter time points ===
# Build index list for rows to remove
# Apply filtering
absorbance_subset = np.delete(absorbance_subset, time_filter_indices, axis=0)
timestamps_filtered = np.delete(timestamps, time_filter_indices)
# --- Create 3 plots ---
fig, axs = plt.subplots(1, 3, figsize=(18, 5))
# === 1. Heatmap of absorbance over time and wavelength ===
X, Y = np.meshgrid(timestamps_filtered, wavelengths_subset) # Create grids for contour plot
contour = axs[0].contourf(X, Y, absorbance_subset.T, levels=30, cmap="coolwarm")
axs[0].set_title("Experimental Absorbance Data")
axs[0].set_xlabel("Time (s)")
axs[0].set_ylabel("Wavelength (nm)")
fig.colorbar(contour, ax=axs[0]) # Add colorbar to show absorbance scale
# === 2. Mean absorbance over time ===
mean_absorbance = np.mean(absorbance_subset, axis=1)
axs[1].plot(timestamps_filtered, mean_absorbance,
label=f"Mean absorbance ({wavelengths_subset[0]:.0f}-{wavelengths_subset[-1]:.0f} nm)",
color='tab:blue')
axs[1].set_title("Mean Absorbance Over Time")
axs[1].set_xlabel("Time (s)")
axs[1].set_ylabel("Absorbance")
axs[1].tick_params(axis="x", rotation=45)
axs[1].legend()
axs[1].grid(True)
# === 3. Compare start and end absorbance spectra ===
axs[2].plot(wavelengths_subset, absorbance_subset[0, :], label="Spectrum at $t=0$", color='red')
axs[2].plot(wavelengths_subset, absorbance_subset[-1, :], label="Spectrum at $t=end$", color='blue')
axs[2].set_title("Absorbance Spectra")
axs[2].set_xlabel("Wavelength (nm)")
axs[2].set_ylabel("Absorbance")
axs[2].legend()
axs[2].grid(True)
# Improve layout spacing
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
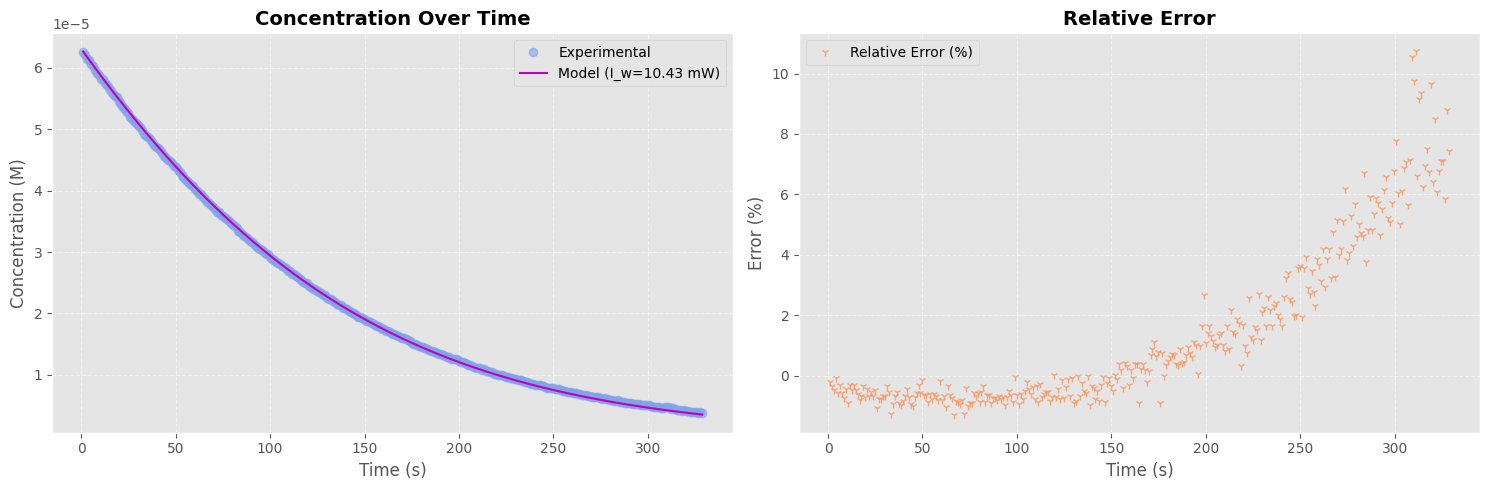
Kinetic Modeling and LED Power Estimation#
This section fits the photokinetics model to the experimental concentration curve derived from absorbance data, to estimate the effective LED power.
Assumes first-order photon absorption
Uses
scipy.integrate.solve_ivpfor integrationFits using
curve_fitwith LED power as a free parameter
# === USER PARAMETERS ===
wl = 505 # nm (LED wavelength)
volume = 14e-4 # L
l = 1 # cm (optical path length)
eps_closed_505 = 0.6e4 # M^-1.cm^-1
eps_closed_562 = 1.1e4 # M^-1.cm^-1
I_w_initial_guess = 14.27e-3 # Initial guess (W)
QY_CF2OF = np.power(10, -2.67 + 526 / wl) # Quantum yield estimation from literature
print(f"Quantum Yield (QY_CF2OF): {QY_CF2OF:.4f}")
from scipy.integrate import solve_ivp
from scipy.optimize import curve_fit
# === Physics constants ===
h = 6.62607004e-34 # Planck constant (J.s)
NA = 6.02214086e23 # Avogadro number (mol^-1)
c_vacuum = 299792458 # m/s
v = c_vacuum / (wl * 1e-9) # Frequency (Hz)
# === Experimental concentration from absorbance ===
C_exp = mean_absorbance / (eps_closed_562 * l)
C0 = C_exp[0]
# === ODE definition ===
def dC_dt(t, C_closed, I_w):
I_0 = I_w / (h * v * NA) / volume # Photon flux [mol photons / L]
I_abs = I_0 * (1 - np.exp(-eps_closed_505 * C_closed * l * np.log(10)))
return -QY_CF2OF * I_abs
# === Fitting function wrapper ===
def model(t, I_w, offset):
sol = solve_ivp(dC_dt, [t[0], t[-1]], [C0], t_eval=t, args=(I_w,))
if not sol.success:
print("⚠️ ODE solver failed:", sol.message)
return np.full_like(t, np.nan)
return sol.y[0] + offset
# === Fit parameters ===
initial_guess = (I_w_initial_guess, 0)
bounds = ([0, -1], [100e-3, 1]) # Bounds for I_w and offset
print("=== Starting curve fit ===")
popt, pcov = curve_fit(model, timestamps_filtered, C_exp, p0=initial_guess, bounds=bounds)
uncertainties = np.sqrt(np.diag(pcov))
# === Report fitted parameters ===
print("\n=== Fit Results ===")
params = ["I_w (W)", "Offset (M)"]
for name, val, err in zip(params, popt, uncertainties):
print(f"{name}: {val:.6f} ± {err:.6f}")
# === Compute fitted curve ===
fitted_values = model(timestamps_filtered, *popt)
# === Plotting ===
fig, axs = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=(15, 5))
colors = ["#81a3e8", "#f9955e", "m"]
# Plot: Concentration vs Time
axs[0].plot(timestamps_filtered, C_exp, "o", color=colors[0], label="Experimental", alpha=0.6)
axs[0].plot(timestamps_filtered, fitted_values, "-", color=colors[2], label=f"Model (I_w={popt[0]*1e3:.2f} mW)")
axs[0].set_title("Concentration Over Time", fontsize=14, fontweight="bold")
axs[0].set_xlabel("Time (s)")
axs[0].set_ylabel("Concentration (M)")
axs[0].grid(True, linestyle="--", alpha=0.5)
axs[0].legend()
# Plot: Relative Error
relative_error = (C_exp - fitted_values) * 100 / C_exp
axs[1].plot(timestamps_filtered, relative_error, "1", color=colors[1], label="Relative Error (%)", alpha=0.8)
axs[1].set_title("Relative Error", fontsize=14, fontweight="bold")
axs[1].set_xlabel("Time (s)")
axs[1].set_ylabel("Error (%)")
axs[1].grid(True, linestyle="--", alpha=0.5)
axs[1].legend()
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
Quantum Yield (QY_CF2OF): 0.0235
=== Starting curve fit ===
=== Fit Results ===
I_w (W): 0.010431 ± 0.000024
Offset (M): 0.000000 ± 0.000000